Draw A Longitudinal Wave
Draw A Longitudinal Wave - The pattern is best seen by doing one particle at a time. Transverse waves longitudinal waves what are transverse waves? Study the definitions and examples of each type of wave, and examine longitudinal and. Web tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave diagram. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. The diameter is 2 times the radius, so c = 2πr. Web however, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although fig. 1 is a perfectly valid plot of ˆ, it does not indicate what the wave actually looks like. Drawing longitudinal waves by plotting the displacements of individual particles through which a wave is passing, students can develop their ideas of the underlying process of a wave. Students should use a particle spacing of 1 cm. Web a type of longitudinal wave: Web longitudinal waves and transverse waves. This video answers the following questions:. Web longitudinal waves are waves in which the motion of the individual particles of the medium is in a direction that is parallel to the direction of energy transport. In transverse waves, the displacement of the particle is perpendicular to the direction. Drawing longitudinal waves by plotting the displacements of individual particles through which a wave is passing, students can develop their ideas of the underlying process of a wave. There is no transverse motion, so the system simply lies along a straight line. They simply oscillate back and forth about their individual equilibrium positions. Properties of periodic waves (opens a modal). In transverse waves, the displacement of the particle is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. The pattern is best seen by doing one particle at a time. Mechanical waves are categorized by their type of motion and fall into any of two categories: 2π radians = 360 degrees. A longitudinal wave can be created in a slinky. The pattern is best seen by doing one particle at a time. Note that both transverse and longitudinal waves can be periodic. There is no transverse motion, so the system simply lies along a straight line. A plane pressure pulse wave. Web in a longitudinal wave the particle displacement is parallel to the direction of wave propagation. Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. They simply oscillate back and forth about their individual equilibrium positions. The meaning of this is that any angle can be expressed in radians as. Transverse waves longitudinal waves what are transverse waves? Web longitudinal waves and transverse waves. This time the displacement of a single point in the medium is parallel to the direction of the motion of the wave, the defining characteristic of a longitudinally polarized wave. Web longitudinal waves propagate parallel to the direction of the particle in the medium. What changes. From sunshine to wifi to regulating our heartbeats, this physics phenomenon shapes our lives and our world in so many ways. The diameter is 2 times the radius, so c = 2πr. The particles do not move down the tube with the wave; One way to remember the movement of particles in longitudinal waves is to use the 'p' sound:. Speed at which the wave disturbance moves. Mechanical waves are categorized by their type of motion and fall into any of two categories: Web longitudinal waves and transverse waves. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. The meaning of this is that any angle can be expressed in radians as an arclength on a circle. A plane pressure pulse wave. As a mechanical wave, longitudinal waves always require a medium to propagate. Web a longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. , the vibrations are parallel. Speed at which the wave disturbance moves. A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length, followed by a stretching; The particles do not move down the tube with the wave; Students should use a particle spacing of 1 cm. Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration. Web however, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although fig. And rarefaction close rarefaction an area of reduced pressure. Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. The diameter is 2 times the radius, so c = 2πr. Study the definitions and examples of each type of wave, and examine longitudinal and. Speed at which the wave disturbance moves. Drawing longitudinal waves by plotting the displacements of individual particles through which a wave is passing, students can develop their ideas of the underlying process of a wave. This time the displacement of a single point in the medium is parallel to the direction of the motion of the wave, the defining characteristic of a longitudinally polarized wave. A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length, followed by a stretching; The pattern is best seen by doing one particle at a time. You could therefore draw the wave by. Web the circumference of a circle = π times its diameter. A longitudinal wave can be created in a slinky if the slinky is stretched out in a horizontal direction and the first coils of the slinky are vibrated horizontally. Mechanical waves are categorized by their type of motion and fall into any of two categories: There is no transverse motion, so the system simply lies along a straight line. In transverse waves, the displacement of the particle is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
PPT Chapter 11 Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1901329
[Solved] Draw a longitudinal wave and label the following properties

Diagram Of Wave

Oscillations and Waves online presentation

PPT Chapter 17 Mechanical Waves & Sound PowerPoint Presentation ID
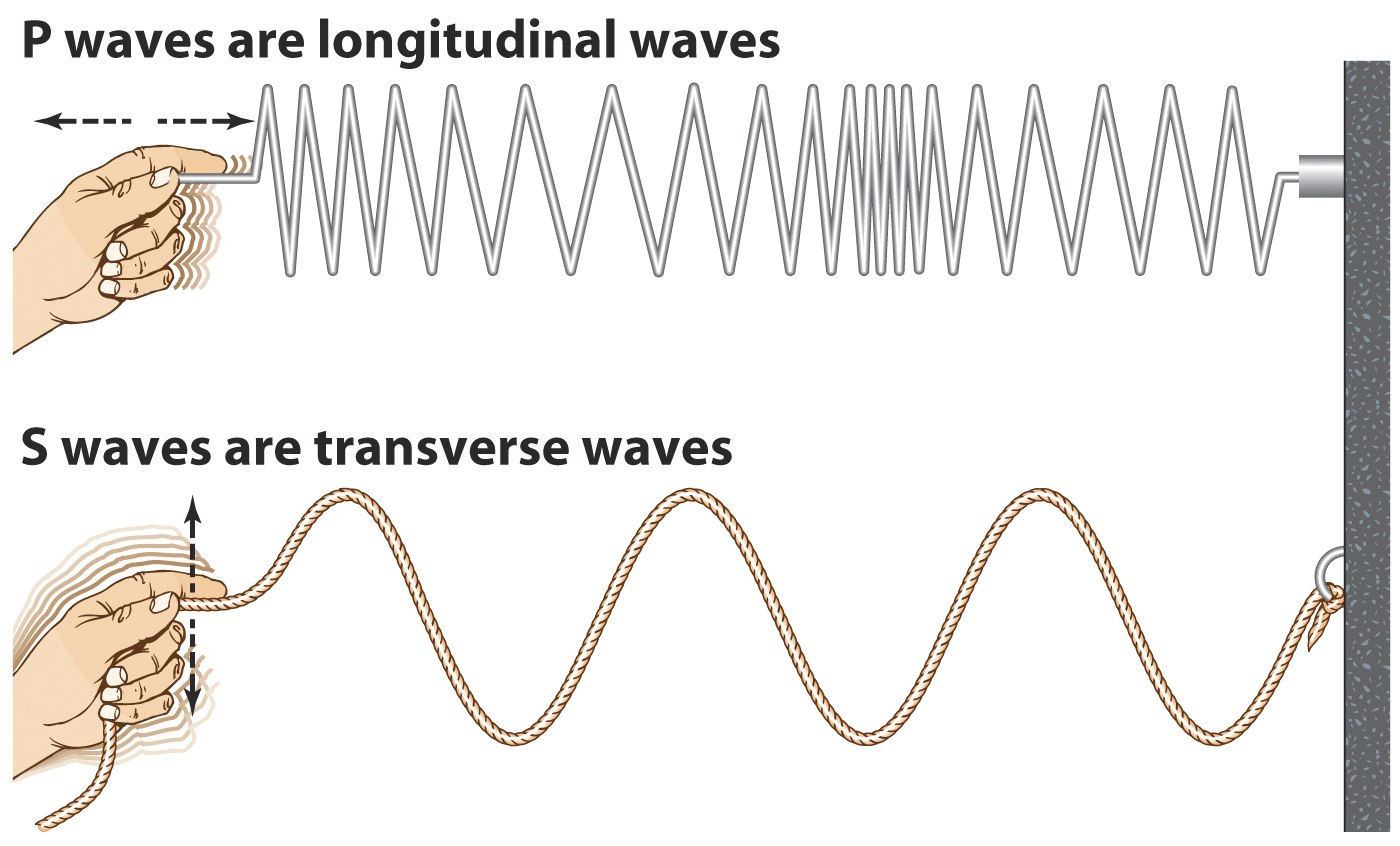
Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and

PPT A longitudinal wave is PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Waves Class 11 Notes, Formulas, NCERT, For NEET Leverage Edu

Wave, its types and characteristics Online Science Notes

Longitudinal Waves and Labelling wave diagrams YouTube
From Sunshine To Wifi To Regulating Our Heartbeats, This Physics Phenomenon Shapes Our Lives And Our World In So Many Ways.
What Changes Is The Density Along The Line.
Web In A Longitudinal Wave The Particle Displacement Is Parallel To The Direction Of Wave Propagation.
Web Learn About Transverse Waves Vs.
Related Post: