Brain And Spinal Cord Drawing
Brain And Spinal Cord Drawing - Web name the major areas of the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain, and describe their main functions. From the periphery to the central nervous system via afferent neurons, and from the central nervous system to the periphery via efferent neurons. According to some estimates, females have a spinal cord of about 43 centimeters (cm), while males have a spinal cord. Web the brainstem, illustrated in figure 42.4.3 42.4. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and vertebral column growth. Web the module promotes learning and mastery of spinal cord anatomy and lesion localization. Web the brain and the spinal cord are the central nervous system, and they represent the main organs of the nervous system. The cerebrum (prosencephalon or forebrain) comprises the telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres) and the diencephalon. The largest of these three is the forebrain (derived from the prosencephalon in the developing brain). To recognize the principal features of the spinal cord, including the longitudinal organization of spinal segments and internal distinctions among levels. The largest of these three is the forebrain (derived from the prosencephalon in the developing brain). Web name the major areas of the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain, and describe their main functions. Web the central nervous system ( cns) consists of the brain and the spinal cord. One spinal cord specimen available for demonstration purposes Web the brainstem, illustrated in. According to some estimates, females have a spinal cord of about 43 centimeters (cm), while males have a spinal cord. The leathery dura mater is the outermost and toughest layer. The peripheral nervous system ( pns ), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the cns, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons. How to draw. Web the spinal cord extends from the bottom of the medulla and through a large opening in the bottom of the skull. The peripheral nervous system ( pns ), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the cns, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons. Web the module promotes learning and mastery of spinal cord anatomy. Identify the anatomical and functional divisions of the cortex. Describe the anatomy and function of the corpus callosum. The cerebrum, the diencephalon, the brain stem, and the cerebellum. Web anatomy the spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (cns). From the periphery to the central nervous system via afferent neurons, and from the central nervous system to the. Identify the hemispheres and lobes of the brain. Web the brain generates commands for target tissues and the spinal cord acts as a conduit, connecting the brain to peripheral tissues via the pns. Web if the cns is the processing centre of the human body, the brain is its headquarters. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and. Web information travels in two directions: It is in the cns that all of the analysis of information takes place. Web the brainstem, illustrated in figure 42.4.3 42.4. Central nervous system anatomical poster for neurology clinic. The peripheral nervous system ( pns ), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the cns, includes sensory neurons. The brain is divided into the cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, and brainstem. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and vertebral column growth. 3, connects the rest of the brain with the spinal cord. Web both the brain and spinal cord are covered by three layers of tissue (meninges) that protect them: To recognize the principal features of the. Identify the hemispheres and lobes of the brain. The leathery dura mater is the outermost and toughest layer. Created by matthew barry jensen. According to some estimates, females have a spinal cord of about 43 centimeters (cm), while males have a spinal cord. Describe the anatomy and function of the corpus callosum. Web anatomy the spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (cns). It is in the cns that all of the analysis of information takes place. To recognize the principal features of the spinal cord, including the longitudinal organization of spinal segments and internal distinctions among levels. How to draw a the human brain easy and step by step.. Motor and sensory neurons extend through the brainstem allowing for the relay of signals between the brain and spinal cord. Web this human anatomy clipart gallery offers 265 illustrations of the central nervous system, including external and dissected views of the brain and spinal cord. Web the central nervous system ( cns) consists of the brain and the spinal cord.. The cerebrum (prosencephalon or forebrain) comprises the telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres) and the diencephalon. Identify the hemispheres and lobes of the brain. One spinal cord specimen available for demonstration purposes The largest of these three is the forebrain (derived from the prosencephalon in the developing brain). Identify the anatomical and functional divisions of the cortex. The thin pia mater is the innermost layer, which adheres to the brain and spinal cord. Forebrain, endbrain , show more. Web the module promotes learning and mastery of spinal cord anatomy and lesion localization. Functionally, the pns is further subdivided into two functional divisions; Web anatomy the spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (cns). To recognize the principal features of the spinal cord, including the longitudinal organization of spinal segments and internal distinctions among levels. Web anatomy the length of the spinal cord varies from person to person. Describe the anatomy and function of the corpus callosum. Web the spinal cord extends from the bottom of the medulla and through a large opening in the bottom of the skull. The brain is a remarkably complex organ comprised of billions of interconnected neurons and glia. The midsagittal section of the brain shows the three major parts of the brain, which are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.Human Brain And Spinal Cord Illustration HighRes Vector Graphic

The coverings of the brain and spinal cord. (A) The brain and spinal

The spinal cord Queensland Brain Institute University of Queensland

Brain Anatomy Spinal Cord Stock Illustration Illustration of

Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts and Spinal Cord Functions

Illustration, human brain, spinal cord Stock Image C005/6988
Human Brain And Spinal Cord Artwork HighRes Vector Graphic Getty Images

Duke Neurosciences Lab 2 Spinal Cord & Brainstem Surface and

Anatomy Of Spinal Cord Brain Anatomy Spine Anatomi manusia, Tubuh
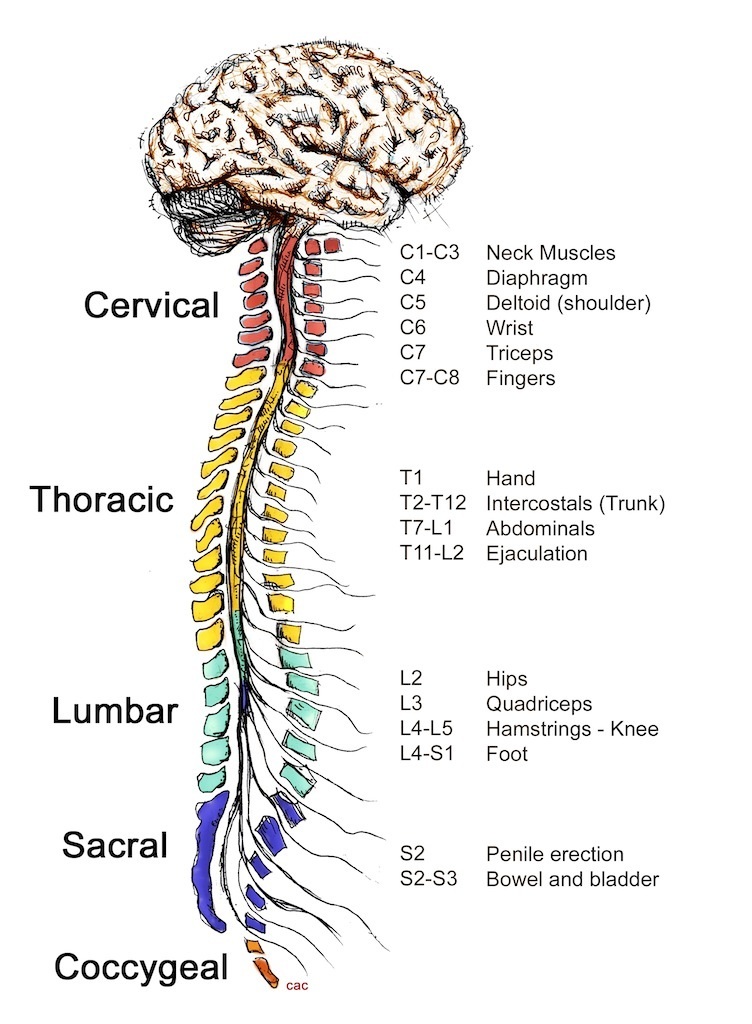
How the spinal cord works Reeve Foundation
Web This Human Anatomy Clipart Gallery Offers 265 Illustrations Of The Central Nervous System, Including External And Dissected Views Of The Brain And Spinal Cord.
Created By Matthew Barry Jensen.
Explain Brain Lateralization And Give Examples Of Lateralization In Humans.
Web Information Travels In Two Directions:
Related Post: